Going Forward
The DRIVEMODE concept stems from the idea of integrating technologies (used in electrical machines and in power electronics) to provide highly efficient and compact integrated modular drivetrain components dedicated to different kinds of cars. These include mass produced electric and hybrid vehicles, low performance and high performance vehicles and different types of heavy-duty vehicles.
Understanding the core
The main components of DRIVEMODE shown in Figure 1 are as follows: (A) High-speed gearbox, (B) High-speed motor and (C) Silicon Carbide (SiC) inverter. They are all integrated together as one compact integrated drivetrain module (IDM) together with a high-voltage battery, controls and a cooling unit. The main components have the following features:
High-speed gearbox
- Speed: 15-20 krpm to ~1.5-2.5krpm
- Power: up to 90 kW
High-speed motor
- Power: 35-60 kW (70-90 kW peak)
- Speed: 15-20 krpm
SiC inverter
- Frequency: >20 kHz
- Voltage: 800V DC
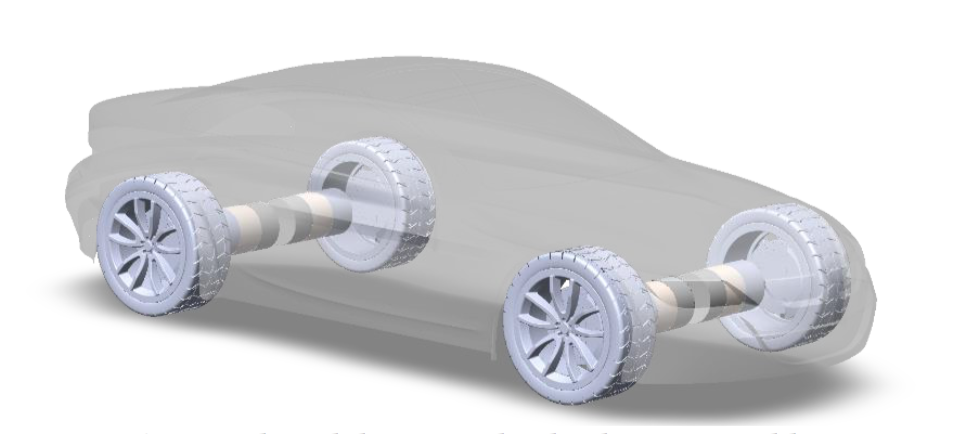
Distributed drive concept: each wheel is powered by its own integrated drivetrain module
Advantages of these set-up include
- The high-frequency power convertor and the high-speed electrical motor will reduce the materials costs and footprint.
- The SiC semiconductor will gradually decrease the switching loses, which will improve the efficiency significantly while enabling the cars the drivetrain to operate at higher frequencies.
- The usage of high-voltage (600-900V) battery will decrease the required copper weight, therefore, simplifying the operation of the motor at high speeds and improving the efficiency of the SiC drive and reducing the charging times.
Due to all these, our drivetrain modules will be mass-produced easily and will influence dramatically the stability control and the way cars are steered and braked.
The partners
DRIVEMODE is led by the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland and is composed by 12 partners from 6 different EU member states: Semikron Elektronik GMBH & Co. KG, AVL Trimerics GMBH and Technische Universitaet Ilmenau (Germany), Visedo Oy (Finland), Chalmers Tekniska Hoegskola AB, National Electric Vehicle Sweden AB and Borgwarner Sweden AB (Sweden), Thien Edrives BMGH (Austria), Univerza V Ljublkani (Slovenia) and, S.C.I.R.E. Consorzio and Fondazione iCons (Italy).
